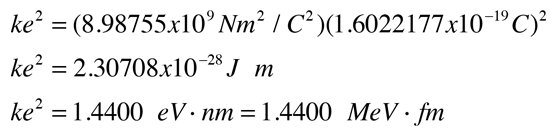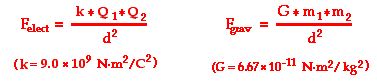K Constant Value Physics
If the charged objects are present in water the value of k can be reduced by as much as a.
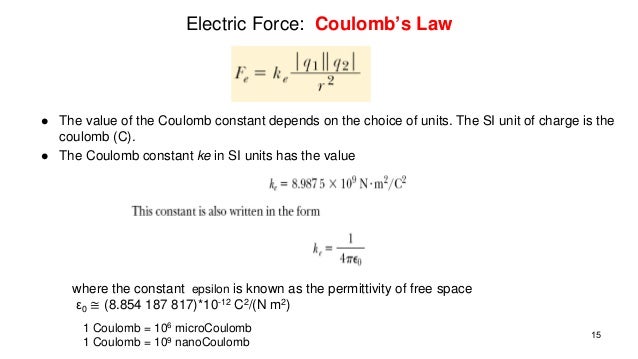
K constant value physics. F which represents force k which is called the spring constant and measures how stiff and strong the spring is and x is the distance the spring is stretched or compressed away from its equilibrium or rest position. Boltzmann constant symbol k a fundamental constant of physics occurring in nearly every statistical formulation of both classical and quantum physics. The variables of the equation are. The value of this constant is dependent upon the medium that the charged objects are immersed in.
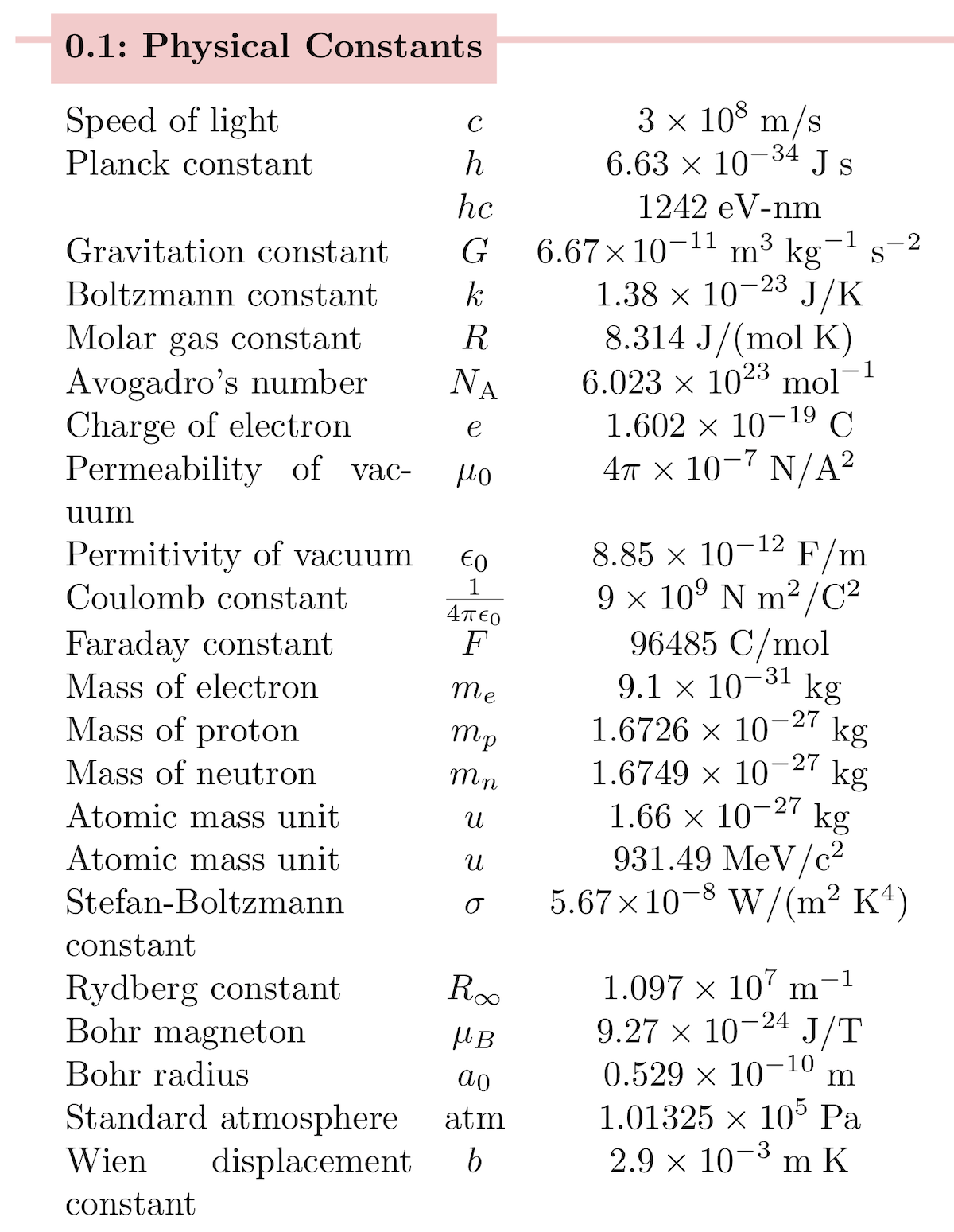
6 0221 x 10 23 mol 1. In si units it is equal to 8 987 551 7923 14 10 9 kg m 3 s 2 c 2. The minus sign shows that this force is in the opposite direction of the force that s stretching or compressing the spring. 10 5 ev k.
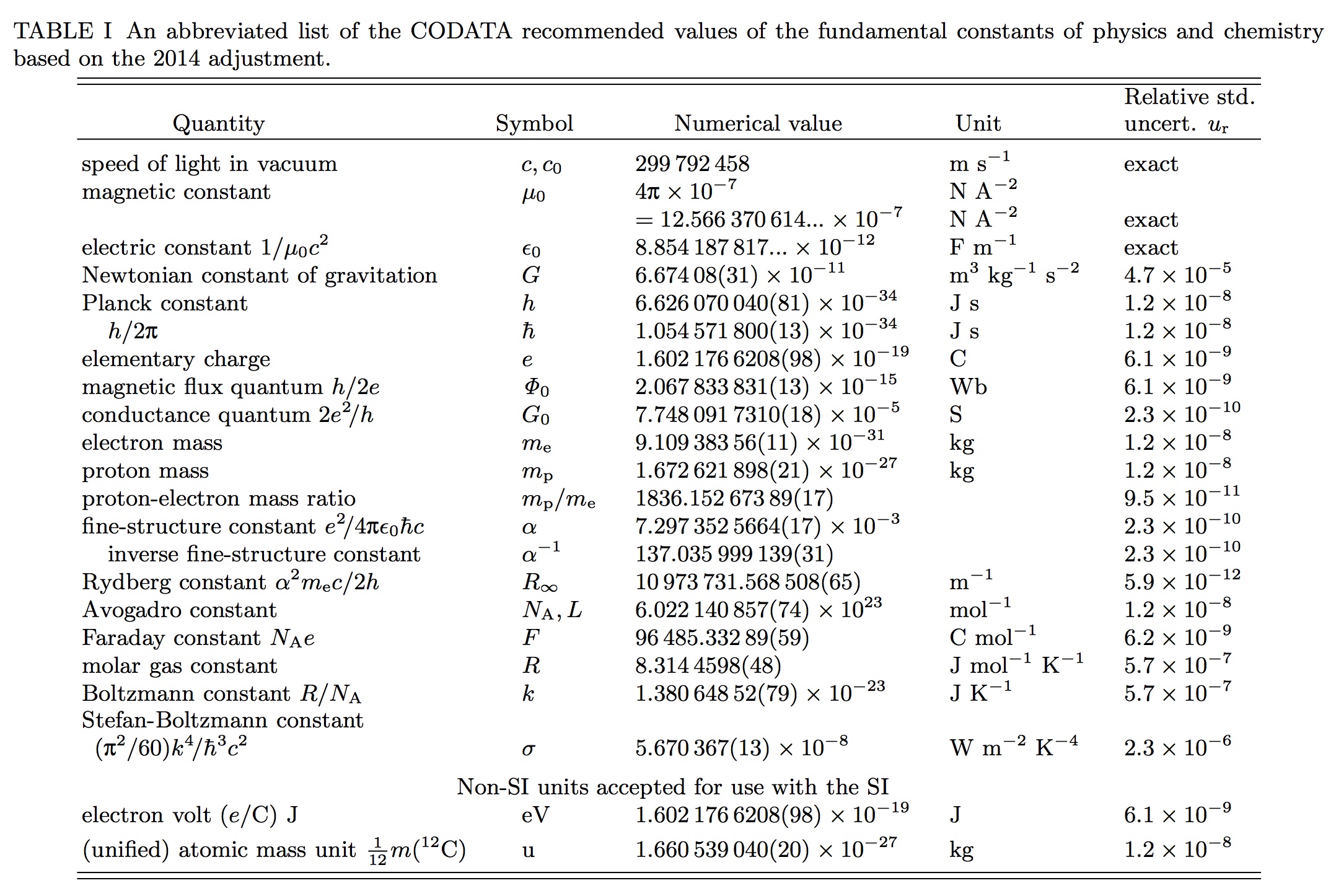
The coulomb constant the electric force constant or the electrostatic constant denoted k e k or k is a proportionality constant in electrostatics equations. It was named after the french physicist charles augustin de coulomb 1736 1806 who introduced coulomb s law. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant and in planck s law of black body radiation and boltzmann s entropy formula the boltzmann constant has the dimension energy divided by temperature. Gerhard fasol in the new si system the value of the boltzmann constant k is defined as exactly k 1 380 649.
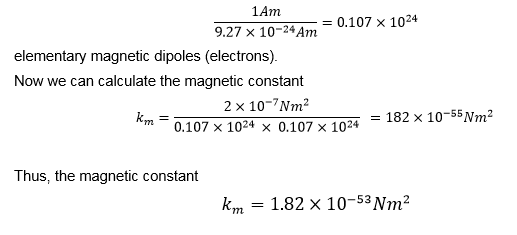
In thermodynamics boltzmann constant is the physical constant relating average kinetic energy of the gas particles and temperature of the gas represented by k or k b the value of boltzmann constant is measured using j k or m 2 kgs 2 k 1 boltzmann constant is one of the seven defining constants that have been given exact definitions. In the case of air the value is approximately 9 0 x 10 9 n m 2 c 2. 10 23 j k or k 8 617 333 262. The constant is named after ludwig boltzmann a 19th century austrian physicist who substantially contributed to the foundation and development of statistical mechanics a branch of theoretical physics.